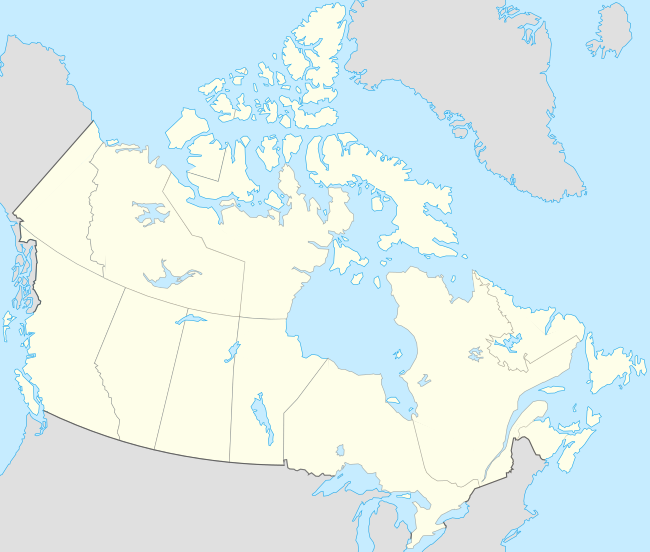
Serveur d'exploration sur la grippe au Canada/Où trouver des faits épidémiques ?
De Wicri Santé
Cette page propose pour chaque province ou territoire du Canada, une liste d'articles classés en fonction de la probabilité d'y trouver des faits épidémiques sur la grippe.
Dans la carte ci dessous, les toponymes pointent vers les pages régionales du wiki et les disques sur les section de cette page.
Sommaire
Alberta
- [73] : When pictures waste a thousand words: analysis of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic on television news.
- [66] : The influence of organizational jurisdiction, organizational attributes, and training measures on perceptions of public health preparedness in Alberta.
- [36] : How rural and urban parents describe convenience in the context of school-based influenza vaccination: a qualitative study.
- [35] : Influenza-like illness-related emergency department visits: Christmas and New Year holiday peaks and relationships with laboratory-confirmed respiratory virus detections, Edmonton, Alberta, 2004-2014.
- [32] : The More the Better? A Comparison of the Information Sources Used by the Public during Two Infectious Disease Outbreaks.
- [28] : Evaluation of the use of oseltamivir prophylaxis in the control of influenza outbreaks in long-term care facilities in Alberta, Canada: a retrospective provincial database analysis.
- [28] : Predicting influenza-like illness-related emergency department visits by modelling spatio-temporal syndromic surveillance data.
- [27] : Public health preparedness in Alberta: a systems-level study.
- [18] : Component-specific effectiveness of trivalent influenza vaccine as monitored through a sentinel surveillance network in Canada, 2006-2007.
- [18] : Assessing the congruence between perceived connectivity and network centrality measures specific to pandemic influenza preparedness in Alberta.
- [18] : Effectiveness of AS03 adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 vaccine: case-control evaluation based on sentinel surveillance system in Canada, autumn 2009.
- [18] : Effectiveness of influenza vaccination in working-age adults with diabetes: a population-based cohort study.
- [18] : Low 2012-13 influenza vaccine effectiveness associated with mutation in the egg-adapted H3N2 vaccine strain not antigenic drift in circulating viruses.
- [18] : Understanding Public Perceptions of the HPV Vaccination Based on Online Comments to Canadian News Articles.
- [17] : Possible basis for the emergence of H1N1 viruses with pandemic potential from avian hosts.
Colombie-Britannique
- [42] : Comparison of the incidence of influenza in relation to climate factors during 2000-2007 in five countries.
- [38] : Beyond Antigenic Match: Possible Agent-Host and Immuno-epidemiological Influences on Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness During the 2015-2016 Season in Canada.
- [36] : Low 2012-13 influenza vaccine effectiveness associated with mutation in the egg-adapted H3N2 vaccine strain not antigenic drift in circulating viruses.
- [36] : Age-Related Differences in Influenza B Infection by Lineage in a Community-Based Sentinel System, 2010-2011 to 2015-2016, Canada.
- [14] : Component-specific effectiveness of trivalent influenza vaccine as monitored through a sentinel surveillance network in Canada, 2006-2007.
- [13] : Association of Parkinson's disease with infections and occupational exposure to possible vectors.
- [12] : Vaccination against 2009 pandemic H1N1 in a population dynamical model of Vancouver, Canada: timing is everything.
- [12] : Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity of an Inactivated Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine Administered Intramuscularly to Children 6 to 35 Months of Age in 2012-2013: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled, Multicenter, Multicountry, Clinical Trial.
- [12] : Influenza vaccine effectiveness against influenza-related hospitalization during a season with mixed outbreaks of four influenza viruses: a test-negative case-control study in adults in Canada.
- [10] : Genetic characterization of seasonal influenza A (H3N2) viruses in Ontario during 2010-2011 influenza season: high prevalence of mutations at antigenic sites.
- [10] : Vaccine Effectiveness Against Lineage-matched and -mismatched Influenza B Viruses Across 8 Seasons in Canada, 2010-2011 to 2017-2018.
- [8] : Review of seasonal influenza in Canada: Burden of disease and the cost-effectiveness of quadrivalent inactivated influenza vaccines.
- [7] : Effectiveness of AS03 adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 vaccine: case-control evaluation based on sentinel surveillance system in Canada, autumn 2009.
- [7] : The influence of organizational jurisdiction, organizational attributes, and training measures on perceptions of public health preparedness in Alberta.
- [7] : Case series of rash associated with influenza B in school children.
Manitoba
- [60] : Reminding and monitoring: new uses of administrative data for preventive care.
- [46] : Communicating risk to aboriginal peoples: first nations and Metis responses to H1N1 risk messages.
- [45] : Effectiveness of influenza vaccination in working-age adults with diabetes: a population-based cohort study.
- [44] : Modelling the transmission dynamics and control of the novel 2009 swine influenza (H1N1) pandemic.
- [44] : Factors influencing H1N1 vaccine behavior among Manitoba Metis in Canada: a qualitative study.
- [40] : No association between 2008-09 influenza vaccine and influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection, Manitoba, Canada, 2009.
- [38] : Exploring reasons for bed pressures in Winnipeg acute care hospitals.
- [33] : Admission to hospital for pneumonia and influenza attributable to 2009 pandemic A/H1N1 influenza in First Nations communities in three provinces of Canada.
- [26] : Social contexts, syndemics, and infectious disease in northern Aboriginal populations.
- [26] : Registry Cohort Study to Determine Risk for Multiple Sclerosis after Vaccination for Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) with Arepanrix, Manitoba, Canada.
- [25] : Transmissibility of the 1918 pandemic influenza in Montreal and Winnipeg of Canada.
- [24] : Did the H1N1 Vaccine Reduce the Risk of Admission with Influenza and Pneumonia during the Pandemic?
- [22] : Simulating the effect of quarantine on the spread of the 1918-19 flu in central Canada.
- [22] : Agent-based modeling of the spread of the 1918-1919 flu in three Canadian fur trading communities.
- [21] : Comparison of the epidemiology of laboratory-confirmed influenza A and influenza B cases in Manitoba, Canada.
Nouveau-Brunswick
- [4] : Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 outbreak at Canadian Forces cadet camp.
- [2] : Increased reactions to pediatric influenza vaccination following concomitant pneumococcal vaccination.
- [1] : EPIDEMIC VIRUS INFLUENZA IN NOVA SCOTIA AND NEW BRUNSWICK DURING THE FIRST SIX MONTHS IN 1963.
- [1] : Genomic relationships of the North American isolate of infectious salmon anemia virus (ISAV) to the Norwegian strain of ISAV.
- [1] : 1951 influenza epidemic, England and Wales, Canada, and the United States.
- [1] : Triple reassortant H3N2 influenza A viruses, Canada, 2005.
- [1] : Baptism of fire: New Brunswick's public health movement and the 1918 influenza epidemic.
- [1] : Toronto's Health Department in action: influenza in 1918 and SARS in 2003.
- [1] : Partial direct contact transmission in ferrets of a mallard H7N3 influenza virus with typical avian-like receptor specificity.
- [1] : Real-time surveillance for respiratory disease outbreaks, Ontario, Canada.
- [1] : Seroprevalence of pandemic influenza H1N1 in Ontario from January 2009-May 2010.
- [1] : Perceived usefulness of syndromic surveillance in Ontario during the H1N1 pandemic.
- [1] : Communicating risk to aboriginal peoples: first nations and Metis responses to H1N1 risk messages.
- [1] : Examining Perceptions about Mandatory Influenza Vaccination of Healthcare Workers through Online Comments on News Stories.
- [1] : Global migration of influenza A viruses in swine.
Île-du-Prince-Édouard
- [2] : Replication of low pathogenic avian influenza virus in naturally infected Mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) causes no morphologic lesions.
- [2] : The challenge of vaccinating adults: attitudes and beliefs of the Canadian public and healthcare providers.
- [1] : One-Health Simulation Modelling: A Case Study of Influenza Spread between Human and Swine Populations using NAADSM.
- [1] : One-Health Simulation Modelling: Assessment of Control Strategies Against the Spread of Influenza between Swine and Human Populations Using NAADSM.
Nouvelle-Écosse
- [29] : The first wave of the 1918 influenza pandemic among soldiers of the Canadian expeditionary force.
- [24] : Influenza revaccination of elderly travelers: antibody response to single influenza vaccination and revaccination at 12 weeks.
- [16] : Comparison of the incidence of influenza in relation to climate factors during 2000-2007 in five countries.
- [14] : Large summertime influenza A outbreak among tourists in Alaska and the Yukon Territory.
- [13] : Divergent evolution of hemagglutinin and neuraminidase genes in recent influenza A:H3N2 viruses isolated in Canada.
- [9] : A composite epidemic curve for seasonal influenza in Canada with an international comparison.
- [8] : Challenges to immunization: the experiences of homeless youth.
- [8] : CSV2018: The 2nd Symposium of the Canadian Society for Virology.
- [7] : The geographic synchrony of seasonal influenza: a waves across Canada and the United States.
- [6] : Use of oseltamivir during influenza outbreaks in Ontario nursing homes, 1999-2000.
- [5] : Estimating influenza deaths in Canada, 1992-2009.
- [4] : Health systems planning for an influenza pandemic.
- [3] : Knowledge, attitudes, beliefs and behaviours of older adults about pneumococcal immunization, a Public Health Agency of Canada/Canadian Institutes of Health Research Influenza Research Network (PCIRN) investigation.
- [3] : Prevalence of influenza A virus in live-captured North Atlantic gray seals: a possible wild reservoir.
- [2] : The community phlebotomy response plan: how does your facility measure up?
- [2] : Lower respiratory tract infections in Inuit infants on Baffin Island.
- [2] : Serologic evidence of influenza A infection in marine mammals of arctic Canada.
- [2] : An IDEA for short term outbreak projection: nearcasting using the basic reproduction number.
- [2] : Bronchiectasis in children from Qikiqtani (Baffin) Region, Nunavut, Canada.
Ontario
- [321] : Toronto's Health Department in action: influenza in 1918 and SARS in 2003.
- [128] : Agent-based modeling of the spread of the 1918-1919 flu in three Canadian fur trading communities.
- [117] : Exploring risk in professional nursing practice: an analysis of work refusal and professional risk.
- [117] : Genetic Characterization of H1N1 and H1N2 Influenza A Viruses Circulating in Ontario Pigs in 2012.
- [103] : Evaluation of a cold/flu self-care public education campaign.
- [92] : Genetic characterization of seasonal influenza A (H3N2) viruses in Ontario during 2010-2011 influenza season: high prevalence of mutations at antigenic sites.
- [89] : Use of oseltamivir during influenza outbreaks in Ontario nursing homes, 1999-2000.
- [85] : Antiviral therapy and outcomes of influenza requiring hospitalization in Ontario, Canada.
- [79] : Suitability and limitations of portion-specific abattoir data as part of an early warning system for emerging diseases of swine in Ontario.
- [76] : Molecular characterization of H3N2 influenza A viruses isolated from Ontario swine in 2011 and 2012.
- [74] : Genetic structure of avian influenza viruses from ducks of the Atlantic flyway of North America.
- [67] : An exploratory spatial analysis of pneumonia and influenza hospitalizations in Ontario by age and gender.
- [63] : The first wave of the 1918 influenza pandemic among soldiers of the Canadian expeditionary force.
- [60] : Economic appraisal of Ontario's Universal Influenza Immunization Program: a cost-utility analysis.
- [58] : Epidemiology of influenza-associated hospitalization in adults, Toronto, 2007/8.
Québec
- [58] : Safety and cross-reactive immunogenicity of candidate AS03-adjuvanted prepandemic H5N1 influenza vaccines: a randomized controlled phase 1/2 trial in adults.
- [53] : Association between the 2008-09 seasonal influenza vaccine and pandemic H1N1 illness during Spring-Summer 2009: four observational studies from Canada.
- [32] : Effectiveness of AS03 adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 vaccine: case-control evaluation based on sentinel surveillance system in Canada, autumn 2009.
- [30] : Predictive validation of an influenza spread model.
- [28] : Molecular and antigenic characterization of triple-reassortant H3N2 swine influenza viruses isolated from pigs, turkey and quail in Canada.
- [23] : Transmissibility of the 1918 pandemic influenza in Montreal and Winnipeg of Canada.
- [22] : Contagious comments: what was the online buzz about the 2011 Quebec measles outbreak?
- [22] : Evolution of a reassortant North American gull influenza virus lineage: drift, shift and stability.
- [22] : Risk of narcolepsy associated with inactivated adjuvanted (AS03) A/H1N1 (2009) pandemic influenza vaccine in Quebec.
- [20] : Cost-effectiveness analysis of antiviral treatment in the management of seasonal influenza A: point-of-care rapid test versus clinical judgment.
- [18] : Component-specific effectiveness of trivalent influenza vaccine as monitored through a sentinel surveillance network in Canada, 2006-2007.
- [17] : The first wave of the 1918 influenza pandemic among soldiers of the Canadian expeditionary force.
- [16] : Risk factors for hospitalization and severe outcomes of 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza in Quebec, Canada.
- [16] : Cost-effectiveness of 2 + 1 dosing of 13-valent and 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Canada.
- [16] : School absenteeism as an adjunct surveillance indicator: experience during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic in Quebec, Canada.
Saskatchewan
- [52] : Human infection with a triple-reassortant swine influenza A(H1N1) virus containing the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase genes of seasonal influenza virus.
- [20] : Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus A (H7N3) in domestic poultry, Saskatchewan, Canada, 2007.
- [15] : Antibiotic prescribing for Canadian preschool children: evidence of overprescribing for viral respiratory infections.
- [12] : The challenge of vaccinating adults: attitudes and beliefs of the Canadian public and healthcare providers.
- [10] : A province-level risk factor analysis of fluoroquinolone consumption patterns in Canada (2000-06).
- [8] : Characteristics of respiratory viral infections during influenza season in Canadian Hutterite Communities.
- [8] : Disease risks associated with free-ranging wild boar in Saskatchewan.
- [7] : Canada's inter-agency wild bird influenza survey.
- [7] : Genetic structure of avian influenza viruses from ducks of the Atlantic flyway of North America.
- [6] : Canadian province-level risk factor analysis of macrolide consumption patterns (2000-2006).
- [6] : The More the Better? A Comparison of the Information Sources Used by the Public during Two Infectious Disease Outbreaks.
- [5] : Temporal aggregation impacts on epidemiological simulations employing microcontact data.
- [4] : Depopulation of the Northern Plains Natives.
- [4] : Influenza and pneumococcal vaccination in Canada and the United States, 1980-1993: what can the two countries learn from each other?
- [4] : Social contexts, syndemics, and infectious disease in northern Aboriginal populations.
Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador
- [20] : Genetic structure of avian influenza viruses from ducks of the Atlantic flyway of North America.
- [4] : Evolution of a reassortant North American gull influenza virus lineage: drift, shift and stability.
- [3] : Wild bird influenza survey, Canada, 2005.
- [3] : Nationwide molecular surveillance of pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus genomes: Canada, 2009.
- [3] : 1st Workshop of the Canadian Society for Virology.
- [3] : Self-rated health and reasons for non-vaccination against seasonal influenza in Canadian adults with asthma.
- [2] : Critical care capacity in Canada: results of a national cross-sectional study.
- [2] : The More the Better? A Comparison of the Information Sources Used by the Public during Two Infectious Disease Outbreaks.
- [1] : 1951 influenza epidemic, England and Wales, Canada, and the United States.
- [1] : A comparison of infection control program resources, activities, and antibiotic resistant organism rates in Canadian acute care hospitals in 1999 and 2005: pre- and post-severe acute respiratory syndrome.
- [1] : Canadian survey on pandemic flu preparations.
- [1] : An evaluation of access to health care services along the rural-urban continuum in Canada.
- [1] : Physician privacy concerns when disclosing patient data for public health purposes during a pandemic influenza outbreak.
- [1] : The geographic synchrony of seasonal influenza: a waves across Canada and the United States.
- [1] : Canadian national surveys on pandemic influenza preparations: pre-pandemic and peri-pandemic findings.
Territoires du Nord-Ouest
- [2] : Serologic evidence of influenza A infection in marine mammals of arctic Canada.
- [2] : Inferring infection hazard in wildlife populations by linking data across individual and population scales.
Yukon
- [34] : Large summertime influenza A outbreak among tourists in Alaska and the Yukon Territory.
- [4] : Outbreak of influenza A infection--Alaska and the Yukon Territory, June-July 1998.
- [4] : Update: outbreak of influenza A infection--Alaska and the Yukon Territory, July-August 1998.
- [4] : Outbreak of influenza A infection among travelers--Alaska and the Yukon Territory, May-June 1999.
- [3] : Influenza and pneumococcal vaccination in Canada and the United States, 1980-1993: what can the two countries learn from each other?
- [3] : From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of influenza A infection--Alaska and the Yukon Territory, June-July 1998.
- [3] : From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of influenza A infection among travelers--Alaska and the Yukon Territory, May-June 1999.
- [2] : Influenza B at Fort Yukon: report of an outbreak, 1961.
- [2] : Influenza in travellers to Alaska, the Yukon Territory, and on west coast cruise ships, summer of 1999.
- [2] : Influenza revaccination of elderly travelers: antibody response to single influenza vaccination and revaccination at 12 weeks.
- [2] : Use of an innovative web-based laboratory surveillance platform to analyze mixed infections between human metapneumovirus (hMPV) and other respiratory viruses circulating in Alberta (AB), Canada (2009-2012).
- [2] : The More the Better? A Comparison of the Information Sources Used by the Public during Two Infectious Disease Outbreaks.
- [2] : Self-rated health and reasons for non-vaccination against seasonal influenza in Canadian adults with asthma.
- [1] : Respiratory virus surveillance. FluWatch project, 2000-2001. End of season update.
- [1] : Rates of influenza vaccination in older adults and factors associated with vaccine use: a secondary analysis of the Canadian Study of Health and Aging.