Metadata towards an e-research cyberinfrastructure: The case of French PhD theses
- Authors
- Jacques Ducloy(i), Jean-Paul Ducasse, Muriel Foulonneau, Luc Grivel, Diane Le Hénaff, Yann Nicolas
- (i) INIST / CNRS
- Abstract
- This paper analyses metadata practices and needs in the French research community. It focuses on PhD theses whose life-cycle is totally controlled by the academic institutions. It uses information treatments dealing with setting up research policy as samples for an eresearch orientation. Several case-studies illustrate the fundamental role of various repositories containing affiliations, authorities or linguistic items. ARTIST, the collective author of this paper, is introduced.
Contents
Archived version
Introduction
This paper is the result of a collaborative work and was written by a networked team of people, engineers or librarians, working in different organisations, in the framework of ARTIST[1] (Appropriation par la Recherche des Technologies de l’Information Scientifique et Technique) project. Our first experience was based on various contributions on a terminological forum, about a translation[2] of “What Is a Digital Library anyway, anymore”, a paper written by Carl Lagoze, and whose subject deals with the deep structure of a Digital Library[9]. This paper is a new cooperative experience which would like to analyse how metadata could help the French academic community in building a federative Digital Library.
The annual issue of the “Academic Ranking of World Universities” [6] is causing discomfort in those in charge of setting up research policies. Improving the quality of metadata items such as affiliations is now considered as a key issue for improving the visibility of universities. The researchers themselves are now permanently looking at impact factor. The “publish or perish” notion is now used as a strong incentive for author self-archiving in institutional repositories [4].
Academic librarian and research communities begin to feel that metadata are not only useful for information retrieval but could play a more strategic function. This new way of viewing is perhaps a first step towards a more global analysis about the role of scholarly publishing in what is called “cyberinfrastructure for e-science or e-research” [10].
In this context, this paper will explore how metadata could be used in some activities dealing with research policy in a francophone[3] environment. We have chosen to focus on PhD theses because their life-cycle is fully controlled by academic institutions; but a large part of the discussion could be applied to all items of scholarly publishing.
We will show that a precise research policy requires sophisticated metadata. In an open archiving framework, the most popular among technical solutions, such as DSpace [12], or Eprints[4], do not require a depositor to provide strongly structured metadata. Most requirements are limited to a basic set of Dublin Core elements in order to be easily harvested. PhD theses are naturally concerned by this goal of improving visibility [5]. We will show that their initial life-cycle requires that metadata should not be merely descriptive but should include some management elements. Indeed, most of the time and more specifically in a French context, several institutions or organisations are concerned and must cooperate.
As for all published items of research, theses metadata must be usable in any portal (national, international, thematic…) that could increase their visibility. They should also be easily handled by informetric tools in order to be picked out in a scientific or strategic watch or for research policy oriented studies. At this level we will show that a key issue is the handling of vocabularies and affiliations.
In the first part of this paper, we will start by introducing the francophone environment. Then we will present several structuring initiatives dealing with PhD thesis production, union catalogues and institutional archives. Finally, we will discuss three case-studies showing various aspects of metadata and vocabularies.
Digital libraries for e-research: an overview of European, francophone and French contexts
Francophone research institutions must position themselves in relation to a variety of existing national and international frameworks.
They take part in international standardisation initiatives. They have to take into account the evolution of standards and practices in the United States and worldwide. Additionally, they are part of both linguistic and regional networks. France and Belgium for instance are part of both Europe and the francophone area (Francophony). Algeria, Morocco and Tunisia are part of Francophony as well as of the Arabic language community.
As a result, francophone research actors must coordinate with a number of initiatives in multiple areas of cooperation. The metadata strategies adopted for scholarly publishing must ensure interoperability of francophone scholarly material in all those networks. They must reflect very diverse administrative situations in the different countries as well as in the regional and international network infrastructures.
International context of e-research
The open access movement and the Open Archives Initiative have encouraged research institutions to make available theses and dissertations on the Web. On the technical side, the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH)[5] makes it possible to share and exchange metadata about scholarly material. This has allowed the creation of an open framework for publishing theses and dissertations. They are integrated into open repositories and shared in larger networks. In France, this led to the creation of the Centre for Direct Scholarly Communication[6] (CCSD), a major initiative aiming at reengineering the processes of scholarly communication, as illustrated below (section 3.2).
In the United States, efforts to create an open digital library framework in the scope of the Digital Library Initiative DLI-I and DLI-II funded by the National Science Foundation have led to such major projects as the National Science Digital Library[7]. NSDL has contributed to the promotion of standards and the development of services based on an open architecture for digital libraries. The Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations (NDLTD)[8] [13] has developed an infrastructure, including processes and workflow for electronic publishing of theses and dissertations. It has raised IPR issues related to ETD (electronic theses and dissertations) publishing. It has also improved repositories technical interoperability by encouraging the use of OAI-PMH and SRU servers. Finally it has improved metadata-related interoperability by adopting the ETD metadata set (ETDMS) [4] developed as a Dublin Core application profile. ETDMS is notably used in the Cyberthèses project (francophone portal for ETD) further described in section 3.1. Alternative metadata formats such as MARC and MODS (Metadata Object Description Schema maintained by the Library of Congress)[9] are also used. The Metadata Working Group of the Texas Digital Library has developed a descriptive application profile for electronic theses and dissertations in MODS[10]. Finally, a number of libraries embed descriptive metadata in METS wrappers (e.g. The Florida Center for Library Automation [11] , or Uppsala University [12]).
The ARTIST project, collective author of the present article, is notably in charge of tracking information on the multiplicity of existing metadata initiatives and their evolution in order to ensure that French and francophone actors benefit from those initiatives. It aims to better coordinate the standardisation efforts in the different networks.
The European context
The European IST (Information Society Technologies) program, like the DLI programs in the US, has focused on the research dimension of information technologies to create an open digital library framework. Several projects, such as the Open Archives Forum[13] [11], have been funded by the European Commission to raise awareness of national players and to investigate the technology issues related to scholarly communication.
The standardisation of the European Research Systems is also supported by the Commission. For instance, EuroCRIS [14] aims at “transforming research information into knowledge” while maintaining and publishing the CERIF [15] (Common European Research Information Format) recommendation
Nevertheless, the major initiatives to concretely build a framework for scholarly communication were launched at national level. The JISC (Joint Information Systems Committee) has funded projects such as Thesis Alive!16 and Daedalus 17 to promote the electronic publishing of theses and dissertations in the UK and the integration of UK institutions in the NDLTD network. SURF (higher education and research partnership organisation for network services and information and communications technology) has supported DARE (Digital Academic Repositories)18 project to modify the infrastructure of provision of academic information in the Netherlands. However, similar initiatives to create comprehensive frameworks for publishing scholarly material at national level do not exist in all European countries.
The European IST priority on Research Networking (IST 2.5.6) will face the challenge of building a framework for publishing scholarly material, at European level. The DRIVER project (2006-2008) coordinated by the University of Athens will help provide this necessary infrastructure for European research. It will be based on the open infrastructure proposed in the scope of the DELOS network of Excellence for digital libraries19 .
In practice, European actors have extremely diverse administrative organisations, inherited from the past. Interoperability between national systems will have to deal with the heterogeneity of the structures of academic and research entities, their dependencies and relations (as detailed below in section 4.2). Additionally, the implementation of a European framework for e-research will have to face the challenge of multilingualism, with particular impacts on metadata creation and the management of terminologies.
The francophone context
Francophone e-research networks also face both organisational and linguistic challenges. For the most part, francophone countries (more than 50 countries over 5 continents) are outside Europe. They have extremely different research infrastructures. Several institutions contribute in structuring this community. For instance, directly related to theses and dissertations, the “Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie” (OIF)20 has funded Cyberthèses (see section 3.1). Several institutions such as the “Agence universitaire de la Francophonie” (AUF)21 and programs related to research infrastructures such as “Système d’Information Scientifique et Technique” (SIST)22 are also helping standardising scholarly publishing in the francophone area.
Many francophone countries actually use multiple languages. They need to implement multilingual systems, with classic constraints in the case of Latin languages and more complex ones in the case of the Arabic language for example. The IMIST (Moroccan Institute for Scientific and Technical information)23 in Morocco will implement a bilingual union catalogue for theses and dissertations24 .
The French context
The French administrative organisation is particularly complex because of the multiplicity of complementary administrative frameworks (an example will be given further in section 4.2). In the last 10 years, no ambitious program has been launched in France to structure scholarly publishing at national level. Public institutions in charge of libraries and scholarly communication such as ABES (Association for Libraries in Higher Education)25 and INIST (Institute for Scientific and Technical Information)26 have essentially initiated operational projects such as an integrated publishing chain from articles deposit to the extraction of key indicators for research. Local initiatives are often disconnected from those operations launched at national level.
As a result, the focus of operations launched by French actors tends to be too narrow to enable the implementation of a digital library for e-research, which would federate scholarly communication at national level.
Several structuring initiatives
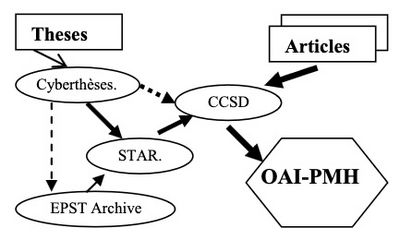
Cyberthèses
Cyberthèses was born within a francophone program which was also extended to South America. Cyberdocs, its related platform, is an open source software which supports an assembly line starting from document writing to dissemination and archiving.
The main members of Cyberthèses network in the Francophony are the following: “Universidad de Chile” in Santiago27 , “Université de Dakar” (Senegal), “Université d’Antananarivo” (Madagascar) and the National Institute of Agronomy of Algiers [1].
In the Cyberthèses project each university is in charge of the conversion of its theses and dissertations into an archiving format (e.g. TEI-lite in XML). At “Université de Lyon 2”, the electronic registration and deposit are now included in the "charte des thèses" which defines the relationship between the student and the institution. The deposit of a complete electronic version of the dissertation is compulsory. The registration is still done by administration, but a workflow software tool was developed which handles the actual deposit and the electronic management of the document and its metadata (DC28 , ETDMS, OAI-PMH).
CCSD: open archive with institutional views
CCSD stands for “Centre de la Communication Scientifique Directe” and aims at promoting direct scientific communication between researchers. Very close to ArXiv’s philosophy, HAL's [16] software provides an interface for authors to upload into the CCSD database their manuscripts of scholarly articles in all fields. Most of the French research organisations have set up a global agreement for a common cooperation based on HAL which can offer an institutional view for any participant.
A specific service called TEL (thèses-EN-ligne) is dedicated to facilitating the self archiving of thesis manuscripts, which are important documents for direct scientific communication between scientists. TEL can be harvested through the OAI-PHM protocol and two metadata formats are available: unqualified Dublin Core30 , and a specific CCSD one. A particular feature of this format deals with formal and precise relationships between authors and affiliations which are clearly identified in deposit procedure. This facility allows the institutional views and illustrates the two main goals of CCSD: open archive with a research management orientation.
STAR: logistic intermediary between local actors and wider actors.
From 2006, the French Ministry of Education, which is responsible for PhD theses infrastructure, will ask ABES, its bibliographic agency, to set up STAR (Signalement des Thèses, Archivage et Recherche), a new service which will operate as a clearing house.
In the input process, STAR will get theses and related metadata from the institutions entitled to guarantee that the given document is true to the original which has been validated by the jury.
In the output process, the digital theses will be delivered to a national digital preservation system which is handled by CINES (Centre Informatique National de l'Enseignement Supérieur)31 . In addition, metadata will be converted to UNIMARC in order to be sent to Sudoc union catalogue which hosts the theses national bibliography.
Several complementary services (figure 1) will be offered to institutions of PhD defence:
- Sending to CCSD/HAL and other bibliographic databases;
- Full text indexing in SUDOC 32 (Système Universitaire de DOCumentation) academic portal;
- Building a permanent identifier (URI) and resolution for guaranteeing access in any location to a valid copy of the thesis.
Thus, through a unique deposit, a local institution will be able to provide long term preservation and dissemination by many channels, with a high level of traceability in both scientific and administrative aspects.
STAR does not claim to dispense with specific tools or workflows set up by universities. It is true that STAR will offer a web interface to those universities that don't possess any local ETDs management tool. For the others, STAR will ingest locally generated metadata and document files. These metadata will comply with the French exchange format TEF.
TEF (Thèses Electroniques Françaises) is a recommendation provided by an AFNOR33 working group (AFNOR CG46/CN357/GE5). It aims at offering a coherent and flexible organisation for rich and normalised theses metadata: bibliographic metadata (DC), rights metadata (METS Rights), administrative metadata relative to the diploma and preservation metadata. Within TEF, FRBR 34 (Functional Requirements for Bibliographic Records) model is used as a conceptual tool to untangle the notion of theses, METS as an XML wrapping to bind the various metadata modules, Schematron35 as a precise and flexible validation tool to enforce the business rules that come from the French context.
STAR, as a tool, like TEF, as a data structure, plays as a go-between for the benefit of those that produce and authenticate the theses and their metadata as well as for those that make use of them.
INIST: Metadata homogenisation
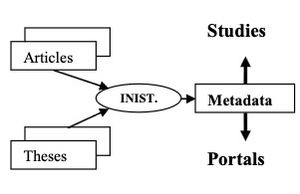
INIST (INstitut de l’Information Scientifique et Technique) is a documentary centre which produces bibliographic databases (Pascal and Francis).
This activity is in permanent evolution. Until fifteen years ago, bibliographic records were manually produced in IS0 2709 format. In a first step, an equivalent SGML DTD was used in order to modernise the production process. Now INIST aims at metadata homogenisation towards a Dublin Core compliant xml schema (Exodic) with automatic indexing.
One of INIST’s departments is specialised in building thematic portal or handling statistical studies dealing with research policies (Figure 2). This entity is more and more implied in defining institutional indicators, bringing INIST, like CCSD, to improve the quality of metadata related to relationships between authors and affiliations.
Three case-studies
Conclusion
For this new experience (the writing of this paper), after the translation of “What Is a Digital Library anyway, anymore”, we have chosen to work again from a quite technical point of view. We have identified a large set of stuff40 , such as theses metadata, affiliation links, vocabulary items, which could upgrade our services. We have underscored the fundamental role of a set of repositories of various items and naming conventions which should complete the classical bibliographic archives…
But “what do we really want to do anyway, anymore?”
Our common objective is to go further in the e-research or e-science movement and to consider scientific and technical information regardless of the global needs of the research organisations. As we are working in separate institutions which manage different objectives or priorities, this job was not an easy one. Perhaps our most interesting result concerns the identification of all compromises that we have to work with:
- Compromise between the national environment of theses and the international network.
- Compromise between the different practices of various actors to ensure reusability of metadata through many applications.
- Compromise between the needs specific to every kind of users: librarians, informetrics engineers, policy actors, social aspects in networked collaborations (with a particular point about evaluation: indeed the thesis status guarantees a validation process which is the last step of semantic web).
- Compromise between a focused look on theses and their integration in a larger environment which goes beyond the basic role of a library, even with a “digital” attribute.
In summary, we would consider the theses as nodes within a constellation containing “articles, dissertations, affiliations, vocabularies”, but also “patents, projects and numerical results”; in other words all components of a CRIS (Current Research Information System) [8]. Because of a current lack of French or francophone federative research programme, such as NSDL, ARTIST is trying to set up a place where field actors could experiment and exchange information about new practices in producing Scientific or Technical Information. We would like to consider this paper as a step towards a more regular activity. At present step ARTIST’s services look like a “collective scientific blog” and now we intend to produce a francophone electronic journal with peer review mechanism, “electronic style” and sophisticated standardisation. The French language is not to be considered as a “limitation” and we think that new concepts must be grown deeper in a native language training area before international confrontation.
In this context, metadata experimentations give us a natural workshop for collaborative activities that we intend to carry on in the framework of DCMI
Acknowledgements
Only the main contributors are listed as authors of this paper. We would like to acknowledge several other people who have contributed by giving some advice or information (Francis ANDRE, Catherine MOREL-PAIR, Clotilde ROUSSEL and Pierrette PAILLASSARD from INIST; Amos DAVID from LORIA, Daniel CHARNAY from CCSD; Ghalia MRAHI from IMIST; Estelle BALIAN from “BiodivErSA – Belgium Biodiversity Platform”, or helping in the translation or revising process (Marc RUBIO and Catherine GUNET from INIST).
References
[1] ↑ Y. Bakelli and S. Benrahmoun. Long-term preservation of ETDs in Algeria: discussion through the CERIST Deposit system. In Proceedings of ETD2003. Berlin 2003. <http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/conferences/etd2003/bakelli-yahia/HTML/bakelli.html >
[2] ↑ BiodivERsA. Compendium of Biodiversity Research Funding Agencies in Europe <http://www.eurobiodiversa.org/rich_files/attachments/Compendium%201%20Feb%202006r ev.doc >
[3] ↑ L. Grivel, H. Fagherazzi, P. Fourneret and A. Zerouki. La conception de bases de données infométriques hybrides : analyse de la pratique de trois observatoires européens. In Journées SFBA proceedings Ile Rousse 99. < http://archivesic.ccsd.cnrs.fr/sic_00000464.html>
[4] ↑ S. Harnad. Publish or Perish - Self-Archive to Flourish : The Green Route to Open Access. In ERCIM News January 2006 <http://www.ercim.org/publication/Ercim_News/enw64/harnad.html>
[5] ↑ D. Le Henaff, and C. Thiolon. Gérer et diffuser des thèses électroniques : un choix politique pour un enjeu scientifique. In Documentaliste - Sciences de l’information. 42(4- 5):272-280. October 2005.
[6] ↑ Institute of Higher Education . Academic Ranking of World Universities - Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2005 < http://ed.sjtu.edu.cn/ranking.htm >
[7] ↑ M. Kaiser. New Ways of Sharing and Using Authority Information. In D-lib Magazine, September 2001 <http://www.dlib.org/dlib/november03/lieder/11lieder.html>
[8] ↑ K. Jeffery. CRIS + open access = the route to research knowledge on the GRID. In 71st IFLA General Conference and Council proceedings, Oslo, Norway, 2005 <http://www.ifla.org/IV/ifla71/papers/007e-Jeffery.pdf>
[9] ↑
C. Lagoze, D. Krafft, S. Payette and S. Jesuroga, What Is a Digital Library anyway, anymore? In D-lib Magazine. November 2005.
<http://dx.doi.org/10.1045/november2005-lagoze>
[10] ↑ C. Lynch., Where Do We Go From Here? The Next Decade for Digital Libraries. In D-lib Magazine, July 2005
Notes
- ↑ < http://artist.inist.fr/ >
- ↑ < http://artist.inist.fr/article.php3?id_article=245 >
- ↑ From the French speaking area
- ↑ < http://www.eprints.org/ >
- ↑ < http://openarchives.org >
- ↑ < http://www.ccsd.cnrs.fr/accueil.php3 ?lang=en >
- ↑ < http://www.nsdl.org >
- ↑ <http://www.ndltd.org/index.en.html >
- ↑ < http://www.loc.gov/standards/mods/ >
- ↑ < http://www.tdl.org/projects/metadata/tdlappprofile.pdf >
- ↑ < http://www.fcla.edu/dlini/etd.html >
- ↑ < http://publications.uu.se/theses/index.xsql?lang=en>
- ↑ < http://www.oaforum.org/ >
- ↑ < http://www.eurocris.org/en/ >
- ↑ < http://www.cordis.lu/cerif/home.html >
- ↑ HAL stands for “hyper article en ligne” < http://hal.ccsd.cnrs.fr/?langue=en >