Difference between revisions of "European perch"
imported>Jacques Ducloy |
imported>Jacques Ducloy m (11 revisions imported) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | In order to study the way that is used by Wikipedia about taxonomies this page has been imported from Wikipedia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *European perch. (2010, March 11). In ''Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia''. Retrieved 18:01, April 11, 2010, from http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=European_perch&oldid=349266626 | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Page imported from Wikipedia= | ||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
| name = European perch | | name = European perch | ||
| status = LR/lc | status_system = IUCN2.3 | | status = LR/lc | status_system = IUCN2.3 | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image =PercheCommune1.jpg |
| regnum = [[Animal]]ia | | regnum = [[Animal]]ia | ||
| phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] | | phylum = [[Chordate|Chordata]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 20: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[ | + | The '''European perch''' (''Perca fluviatilis'') is a highly predatory species of [[perch]] found in [[Europe]] and [[Asia]]. In some areas it is known as the '''redfin perch''' or '''English perch''', and it is often referred to by the shortform '''perch'''. The species is very popular and has been widely introduced beyond its native area, into [[Australia]], [[New Zealand]], and [[South Africa]]. They have caused substantial damage to native fish populations in Australia. |
| + | |||
| + | European perch are greenish with red pelvic, anal, and caudal fins. They have 5–9 dark vertical bars on their sides. | ||
| + | |||
| + | European perch size can vary greatly between bodies of water; in Australia the fish are sometimes much larger than in their native Europe. The perch can live for up to 22 years, and older perch are often much larger than average; the maximum recorded length is {{convert|60|cm|abbr=on}} and reach a maximum weight of around {{convert|10.4|kg|abbr=on}} in Australasia{{Citation needed|date=November 2009}}, a maximum of less than {{convert|3|kg|abbr=on}} in the UK (the British record stands at 6lb 2oz), they grow to moderately larger maximums in mainland Europe than in Britain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The perch spawns at the end of April or beginning of May, depositing it upon weeds, or the branches of trees or shrubs that have become immersed in the water; it does not come into condition again until July. The eggs have been known to stick to the legs of wading birds and then transferred to other waters that the birds visit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Taxonomy == | ||
| + | The first scientific description of the river perch was made by [[Artedi, Peter|Peter Artedi]] in 1730. He defined the basic morphological signs of this species after studying perches from Swedish lakes. Artedi described external signs of the perch, count beams of fins, edges and vertebras of the typical perch. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1758 [[Carl Linnaeus]] classified the river perch and named it Perca fluviatilis.<ref name="FB6">{{cite web|url= http://www.fishbase.org/Nomenclature/SynonymsList.php?ID=358&SynCode=29476&GenusName=Perca&SpeciesName=fluviatilis |title= Synonyms of Perca fluviatilis Linnaeus, 1758|work= FishBase|accessdate= 2009-11-23}}</ref> His description was based on Artedi's research. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Fishing == | ||
| + | Baits for perch are minnows, or brandling, red, marsh, and lob worms, shrimps and artificial lures. The tackle should be fine but strong. When using a fish as bait, a trout or pike may occasionally be hooked, therefore the perch angler has a certain responsibility to use a wire trace with such baits as considerable damage could be done to pike or trout if light line is broken. Artificial lures may also be quite effective, particularly for medium sized perch. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Aquarium care== | ||
| + | Keeping of perch requires a large tank and a suitable diet. The tank needs to be thickly planted with plants such as Eleodea, Egeria and others. These must not be introduced to the wild as they are an invasive species. Perch can be kept in ponds with appropriate fish; as with most fish, larger ones may consume fry if they are available. A suitable diet would be earthworms, flakes, silversides and frozen foods such as bloodworm. If fed properly Perch tend to phase away from small fish . | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Relation to the yellow perch== | ||
| + | Because of their similar appearance and ability to cross-breed, the [[yellow perch]] has sometimes been classified as a [[subspecies]] of the European perch, in which case its [[Trinomial nomenclature|trinomial name]] would be ''Perca fluviatilis flavescens''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, it is unclear whether or not [[Hybrid (biology)|hybrids]] are viable, and most classifications treat the two fish as separate species. According to NatureServe, [[allozyme]] data indicates that ''Perca fluviatilis'' and ''Perca flavescens'' are separate species. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == External links == | ||
| + | * {{IUCN2006|assessors=World Conservation Monitoring Centre|year=1996|id=16580|title=Perca fluviatilis|downloaded=12 May 2006}} | ||
| + | * {{ITIS|ID=168470|taxon=Perca fluviatilis|year=2006|date=6 June}} | ||
| + | * [http://www.fishbase.org/Summary/speciesSummary.php?ID=358&genusname=Perca&speciesname=fluviatilis Fishbase.org - European perch] | ||
| + | * [http://www.anglerstimes.co.uk/perch.htm British Record Perch] | ||
| + | * [http://www.amonline.net.au/fishes/fishfacts/fish/pfluviat.htm Redfin Perch – Perca fluviatilis] | ||
| + | * [http://www.tdvan.freeserve.co.uk/Perch%20Details.htm Perch details] | ||
| + | * [http://www.fundp.ac.be/recherche/projets/en/99275103.html Cross-breeding of Yellow and European perch] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Percidae]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Fish of Europe]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Introduced freshwater fish of New Zealand]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Freshwater fish of Australia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Wicri part= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Wicri metadata== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This page is a pilot one for [[Metadata about fish|Wicri metadata about fish]]. | ||
| + | |||
==Interwiki links== | ==Interwiki links== | ||
See European perch on [[wikipedia:European perch|Wikipedia]]. | See European perch on [[wikipedia:European perch|Wikipedia]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[fr:Perche commune]] | [[fr:Perche commune]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 28 June 2017
In order to study the way that is used by Wikipedia about taxonomies this page has been imported from Wikipedia.
- European perch. (2010, March 11). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 18:01, April 11, 2010, from http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=European_perch&oldid=349266626
Contents
Page imported from Wikipedia
| European perch | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Family: | Percidae |
| Genus: | Perca |
| Species: | Template:Str rep |
| Binomial name | |
| Perca fluviatilis Linnaeus, 1758 | |
| |
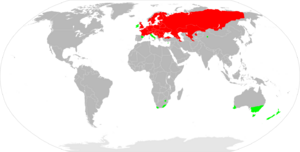
The European perch (Perca fluviatilis) is a highly predatory species of perch found in Europe and Asia. In some areas it is known as the redfin perch or English perch, and it is often referred to by the shortform perch. The species is very popular and has been widely introduced beyond its native area, into Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. They have caused substantial damage to native fish populations in Australia.
European perch are greenish with red pelvic, anal, and caudal fins. They have 5–9 dark vertical bars on their sides.
European perch size can vary greatly between bodies of water; in Australia the fish are sometimes much larger than in their native Europe. The perch can live for up to 22 years, and older perch are often much larger than average; the maximum recorded length is Template:Convert and reach a maximum weight of around Template:Convert in AustralasiaTemplate:Citation needed, a maximum of less than Template:Convert in the UK (the British record stands at 6lb 2oz), they grow to moderately larger maximums in mainland Europe than in Britain.
The perch spawns at the end of April or beginning of May, depositing it upon weeds, or the branches of trees or shrubs that have become immersed in the water; it does not come into condition again until July. The eggs have been known to stick to the legs of wading birds and then transferred to other waters that the birds visit.
Taxonomy
The first scientific description of the river perch was made by Peter Artedi in 1730. He defined the basic morphological signs of this species after studying perches from Swedish lakes. Artedi described external signs of the perch, count beams of fins, edges and vertebras of the typical perch.
In 1758 Carl Linnaeus classified the river perch and named it Perca fluviatilis.[1] His description was based on Artedi's research.
Fishing
Baits for perch are minnows, or brandling, red, marsh, and lob worms, shrimps and artificial lures. The tackle should be fine but strong. When using a fish as bait, a trout or pike may occasionally be hooked, therefore the perch angler has a certain responsibility to use a wire trace with such baits as considerable damage could be done to pike or trout if light line is broken. Artificial lures may also be quite effective, particularly for medium sized perch.
Aquarium care
Keeping of perch requires a large tank and a suitable diet. The tank needs to be thickly planted with plants such as Eleodea, Egeria and others. These must not be introduced to the wild as they are an invasive species. Perch can be kept in ponds with appropriate fish; as with most fish, larger ones may consume fry if they are available. A suitable diet would be earthworms, flakes, silversides and frozen foods such as bloodworm. If fed properly Perch tend to phase away from small fish .
Relation to the yellow perch
Because of their similar appearance and ability to cross-breed, the yellow perch has sometimes been classified as a subspecies of the European perch, in which case its trinomial name would be Perca fluviatilis flavescens.
However, it is unclear whether or not hybrids are viable, and most classifications treat the two fish as separate species. According to NatureServe, allozyme data indicates that Perca fluviatilis and Perca flavescens are separate species.
References
External links
- Template:IUCN2006
- Template:ITIS
- Fishbase.org - European perch
- British Record Perch
- Redfin Perch – Perca fluviatilis
- Perch details
- Cross-breeding of Yellow and European perch
Wicri part
Wicri metadata
This page is a pilot one for Wicri metadata about fish.
Interwiki links
See European perch on Wikipedia.